Dynamic and Static Torque Sensor: What is the different?
FUTEK offers both static (reaction) and dynamic (rotary) torque sensors, which are designed for different applications.

Introduction
Torque Sensors manufactured in US by FUTEK Advanced Sensor Technology (FUTEK), a leading manufacturer producing a huge selection of Torque Transducers, utilizing one of the most advanced technologies in the Sensor Industry: Metal foil strain gauge technology. It is is defined as a transducer used for torque measurement that converts an input mechanical torque into an electrical output signal. Torsions Sensors are also commonly known as Torque Transducer, Torque Cell or Moment Sensor. There are two main types of Torque Sensors: Reaction Torque Sensors or Rotational Torque Sensors.
By definition, torque sensor is a type of transducer, specifically a torque transducer that converts a torque measurement (reaction, dynamic or rotary) into another physical variable, in this case, into an electrical signal that can be measured, converted and standardized. As the torque applied to the sensor increases, the electrical output signal changes proportionally (aka torque detector or torque gauge).

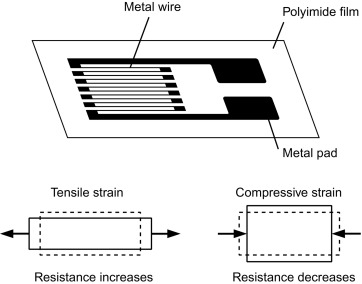
Firstly, we need to understand the underlying physics and material science behind the rotary torque sensor working principle, which is the strain gauge (sometimes referred to as Strain gage). Metal foil strain gauge is a sensor for measuring force whose electrical resistance varies with applied force. In other words, it converts force, pressure (Check our "What is a pressure sensor?" guide), tension, compression, torque, weight (aka weight sensors), etc… into a change in electrical resistance, which can then be measured. This is the basic principle behind how to measure torque.
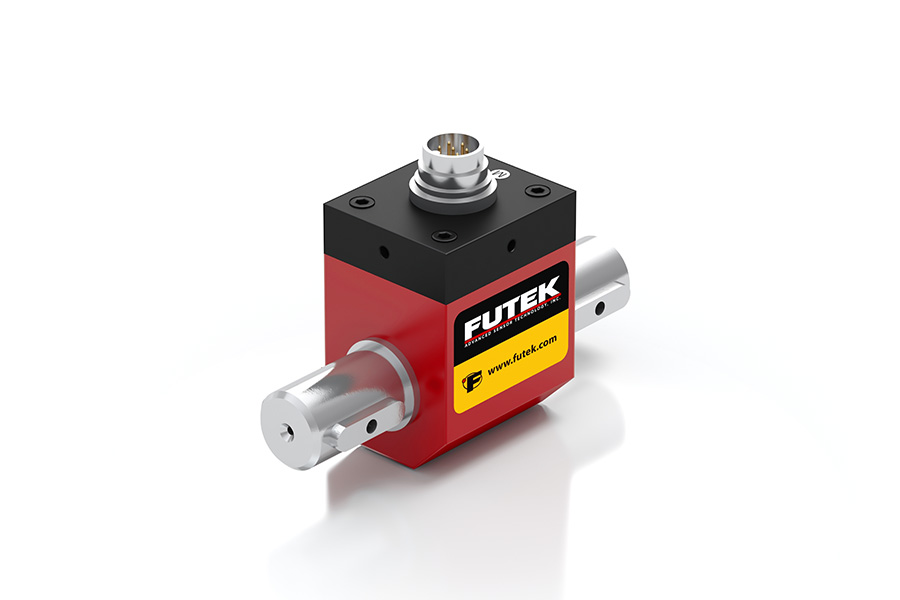
Dynamic (Rotary) torque sensors
- Measures: Rotational torque on a spinning shaft, engine, or motor.
- Sensor type: Rotary torque sensors. These transducers are installed in-line with the spinning shaft.
- How it works: The sensor rotates with the shaft. It uses a slip ring, wireless electronics, or other non-contact methods to transmit the electrical signal from the rotating strain gauges to a stationary display.
- Best for:
- Performance testing on power tools, motors, and turbines.
- Auditing and analyzing the efficiency of test stands, including dynamometers.
- Measuring torque ripple in electric motors.


Static (Reaction) torque sensors
- Measures: Non-rotational or stationary torque.
- Sensor type: Reaction torque sensors. They are installed between the torque-producing device (like a motor) and a fixed, rigid surface. The sensor measures the force that "reacts" to the torque being applied.
- How it works: One side of the sensor is bolted to the ground, and the other is connected to the rotary element. The sensor's internal strain gauges measure the shear forces generated as the element attempts to rotate.
- Best for:
- Auditing the torque of fasteners with a miniature screwdriver.
- Checking the calibration of a torque wrench.
- Testing bearing torque.
- Measuring the stall torque of a motor.
How to choose a Torque Sensor for your application?
A question that we frequently hear is: “What is the right sensor for my application?” The reason why it gets asked so often is that it can be tricky to navigate the various sensor offerings on the market. So, be it a small torque sensor or a high capacity torque sensors (not a string potentiometer), make sure to follow the steps below for adequate torque sensor sizing.
Firstly, understand your application and define the type of torque you want to measure — reaction torque, rotary torque or do you require a dual force torque sensor? Also, what is the environment (temperature, pressure, humidity). The application may require underwater torque sensors accompanied by a pressure transducer. Torque sensors are largely utilized in the automotive industry for product tests and validation (torque sensor automotive).
After you’ve determined that you want to measure torque, define the type of torque you want to measure – reaction torque or rotary torque. Reaction Torque Sensors have no moving parts so they pick up the reaction torque through your system. In the illustrations below you can see where the Rotary Torque Sensor would be used versus a Reaction Torque Sensor in an application involving a motor and break/clutch. Also be sure to define your size requirements (width, height, length, etc) and specification requirements (output, nonlinearity, hysteresis, creep, bridge resistance, temperature range, submersible, environment etc.)




How will you be mounting the sensor? (Flange to flange, square drive, shaft to shaft, hex drive, etc.) Will you be using this clockwise, counterclockwise, or both? Similar to selecting a Load Cell, be sure to select the capacity over the maximum operating torque and determine all extraneous torque and over hung moments, off center prior to selecting the capacity. Note: extraneous torque and moments increase combined stress which will accelerate the fatigue and can affect the performance and accuracy if the correct Torque Sensor / transducer is not selected. For Rotary Torque Sensors you must also specify RPM and seek the assistance of tech support in for proper selection of Slip-Ring or non-contact type. You may also require sensor with built-in encoder for measuring speed and angular deflection or position.
Some sensors outputs a mV/V signal, which can be paired with an amplifier for up to ±10VDC, while other non-contact rotational sensors will provide ±5VDC output. So, if your PLC or DAQ requires analog output, digital output or serial communication, you will need a torque sensor amplifier or signal conditioner. Make sure to select the right strain gage amplifier as well as calibrate the entire measurement system (sensor + signal conditioner). This turnkey solution translates into more compatibility and accuracy of the entire torque measurement system.
Related Products




Technical Sales Support
For more information about our torque and load cell sensors, get in touch with a member of the team, call us now on Penang Office 04-399 7522 or Petaling Jaya 03-7804 7522.